- Common Conditions
- /Elbow

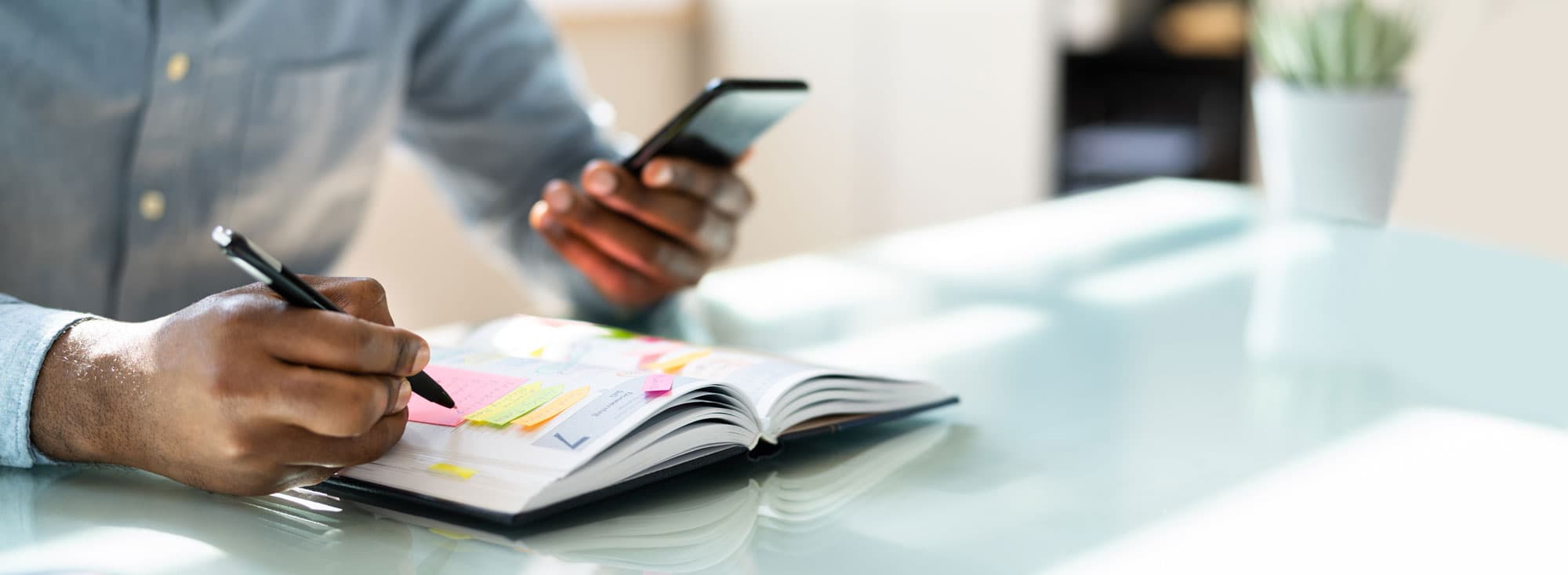
Radial Tunnel Syndrome, also known as radial neuritis, is a confusing and challenging condition affecting the terminal branch of the radial nerve in the arm, the posterior interosseous nerve. It is often misdiagnosed as lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) due to the prevalence of that condition. However, this condition is a constriction or irritation of the posterior interosseous nerve in the proximal, lateral arm.
Pain in the proximal lateral forearm is the most common symptom of radial tunnel syndrome. There is usually not numbness associated with the condition. Radial tunnel syndrome can occur at the same time as lateral epicondylitis, making the diagnosis more confusing. However, the pain is more distal, or toward the hand, than tennis elbow. There is pain with grip, activities and fine control of the fingers. We do not know definitively what causes radial tunnel syndrome, but we believe the posterior interosseous nerve is compressed at the proximal border of the supinator muscle. This muscle has a thick, fibrous tendon-like border that the nerve must travel under, and as the band becomes thicker and therefore less compliant, it can cause constriction of the nerve. Some less common causes are ganglion cysts in the elbow and vascular malformations.
Patients are usually 35-65 years of age, and men and women are affected equally. Radial tunnel syndrome can occur in tennis players and in golfers. It also happens in those with true overuse conditions with repetitive wrist motion, especially rotation.
Generally, physical therapy works most of the time to treat radial tunnel syndrome. Aggressive massage of the area combined with specific exercises will cure radial neuritis most of the time. Surgery is reserved for patients who do not get better with therapy or those with significant weakness, which is a sign of a much more severe compression. Surgery consists of exploration of the nerve and release of the proximal supinator muscle. Some patients will get a temporary worsening of the weakness with surgery, but this almost always recovers.



